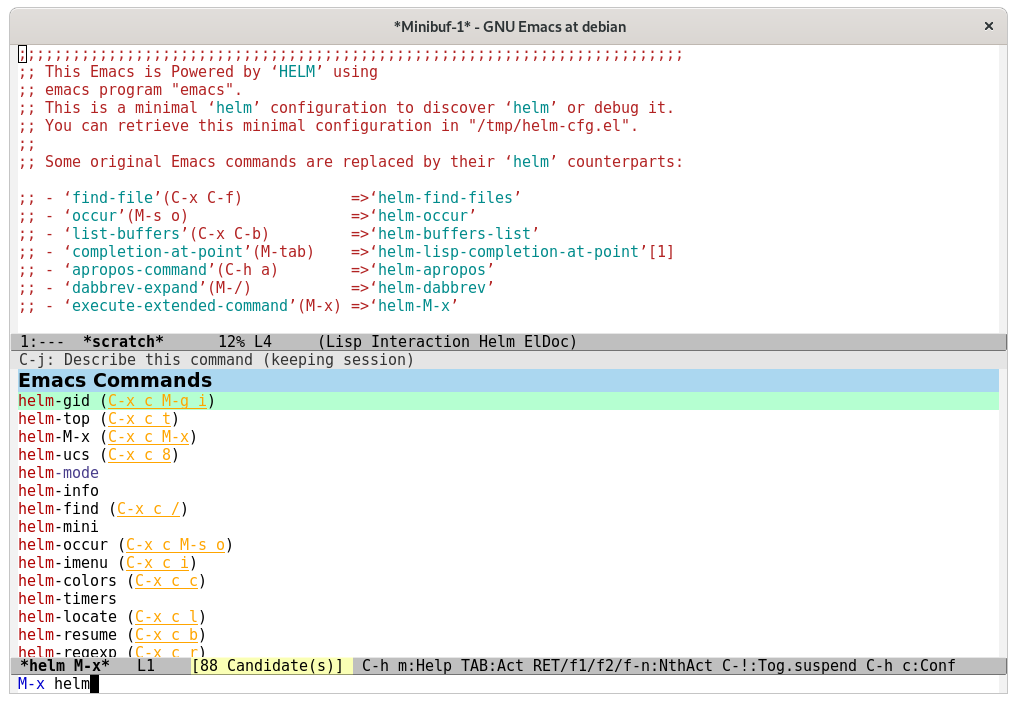
Figure: A typical helm-M-x with
Next: Requirements [Contents][Index]
Helm 3.6.2 and later require
Next: Installation Upgrade and Configuration, Previous: Requirements, Up: Top [Contents][Index]
https://github.com/emacs-helm/helm.git
git@github.com:emacs-helm/helm.git
Next: Introduction, Previous: Download, Up: Top [Contents][Index]
| • Minimal setup using ‘straight.el’ | ||
| • Minimal setup using source | ||
| • Minimal setup using the Package Manager |
‘straight.el’3
Add this to your init file,
(straight-use-package 'helm)
or
# :straight t # :config # […])
(use-package helm :straight t)
For further information, see ‘straight.el’’s user manual.
To upgrade ‘helm’, do M-x straight-pull-package and restart Emacs. ‘straight.el’ will rebuild helm for you.
Next: Minimal setup using the Package Manager, Previous: Minimal setup using ‘straightel’, Up: Installation Upgrade and Configuration [Contents][Index]
Install ‘emacs-async’4 and ‘popup-el’5. Ensure that they
are available in load-path.
If you are using ‘git’,
git clone https://github.com/emacs-helm/helm cd helm make sudo make install
If you have a tarball6,
wget https://github.com/emacs-helm/helm/archive/refs/tags/v3.7.1.tar.gz tar zxvf v3.7.1.tar.gz cd helm-3.7.1/ make sudo make install
Above steps assume that you have installed ‘emacs-async’ is in a standard location. If this is not the case, you need to tell ‘make’ program where it is available using ‘EMACSLOADPATH’7.
git clone https://github.com/emacs-helm/helm cd helm EMACSLOADPATH="/path/to/emacs-async:" make make sudo make install
Above steps
If you want to install ‘helm’ in a path other than ‘/usr/local/’, pass that target path through a ‘PREFIX’ variable.
Add the one of the following to your init file,
(add-to-list 'load-path "/path/to/helm/directory") (require 'helm-config)
or
(add-to-list 'load-path "/path/to/helm/directory") (use-package helm :config (require 'helm-config))
and restart Emacs.
The library ‘helm-config’ loads ‘helm-autoloads.el’. This is essential for having a working install of ‘helm’.
Previous: Minimal setup using source, Up: Installation Upgrade and Configuration [Contents][Index]
Helm is available on MELPA.8
Release version of Helm is available in the stable repository while development version is available in the other repo.
Assuming that you have setup package-archives to include the MELPA,
you can install Helm with M-x package-install RET helm RET.
To upgrade ‘Helm’, use helm-list-elisp-packages. This command is
the Helm equivalent of Emacs’ ‘list-packages’. Using
helm-list-elisp-packages, ensures that ‘helm’ is compiled in a clean
environment.9
Next: Helm Completion vs Emacs Completion, Previous: Installation Upgrade and Configuration, Up: Top [Contents][Index]
People often think helm is just something like ido((Ido)Top) but displaying completion in a vertical layout instead of an horizontal one, it is not, helm is much more powerful than that.
Helm is divided in two distinct categories of commands,
these commands are a fresh implementation of an existing Emacs command and enhance them in useful ways.
these Emacs native commands modified by helm-mode to provide helm completion and only that.
When both are provided e.g switch-to-buffer vs helm-buffers-list
you will prefer the native helm commands generally more featured (more
than one action, allows marking candidates, better display etc…).
Next: General Helm Commands, Previous: Introduction, Up: Top [Contents][Index]
Differences between the two often trip up new users.
Emacs completion is based on the minibuffer. Helm completion is based on the completion window.10 11 12
In standard Emacs, interactivity happens in the minibuffer.
In Helm, interactivity happens in the completion window, not the minibuffer
| • Helm interaction model |
Helm’s interactivity makes the <tab> key redundant for completion because the selection candidates are already made visible in the Helm completion window. So, tab completion is not supported. In Helm, <tab> is used to view available actions to be taken on a candidate.
Because the <tab> key is so ingrained in the muscle memory of long-time Emacs users, transition to Helm’s interactive model requires:
Next: Preconfigured Helm Commands, Previous: Helm Completion vs Emacs Completion, Up: Top [Contents][Index]

Figure: A typical helm-M-x with
Helm’s functionality needs only a few general key bindings as shown below. These are also documented in the mode line.
helm-select-action)lists available actions
helm-execute-persistent-action)invokes the persistent action
helm-toggle-visible-mark-backward) or C-SPC (helm-toggle-visible-mark-forward) or C-@ (helm-toggle-visible-mark)marks a candidate
helm-help)displays the embeded help in an org buffer without quitting helm session.
runs the first action of action list
| • Yanking text |
Up: General Helm Commands [Contents][Index]
Yank symbol at point from helm-current-buffer (i.e. buffer where a
helm command was invoked):
helm-yank-text-at-point)Append word next to point to the minibuffer and advance to next word
(helm-yank-text-at-point ARG)
Yank text at point in ‘helm-current-buffer’ into minibuffer.
helm-undo-yank-text-at-point)Undo last
insertion and rewind yank point in helm-current-buffer
Undo last entry added by ‘helm-yank-text-at-point’.
Next: Helm Mode, Previous: General Helm Commands, Up: Top [Contents][Index]
Invoke M-x helm-M-x RET and type ‘helm’ to discover Helm commands. The ‘Menu Bar -> Helm’ menu item is another way to discover helm commands.
helm-command-prefix-keyStandard Value: “C-x c”
The key ‘helm-command-prefix’ is bound to in the global map.
helm-minibuffer-history-keyStandard Value: “C-r”
The key ‘helm-minibuffer-history’ is bound to in minibuffer local maps.
helm-command-prefix-key (default value C-x c) is the
prefix for the preconfigured helm menu.
helm-command-prefix-key followed by any regular Emacs key invokes
the Helm version of the same command.
For example,
helm-M-x, which is the helm
version of M-x (execute-extended-command).
helm-find-files, which
is the helm version of C-x C-f (find-file).
To run the helm version of a command with a key binding, but without
also typing C-x c) (helm-command-prefix-key), add the
following to your init file.
(global-set-key (kbd "M-x") 'helm-M-x)
Next: Helm With Other Emacs Extensions, Previous: Preconfigured Helm Commands, Up: Top [Contents][Index]
helm-mode enables Helm completion globally for any Emacs command
using completing-read or read-file-name.
helm-mode completes with completion-at-point and implements
completion-in-region-function for completing-read-multiple for
Emacs 24.4 and later.
Helm provides generic functions for completions to replace tab-completion in Emacs with no loss of functionality. To use Helm’s generic functions, first set them in your init file, e.g.:
(global-set-key (kbd "M-x") #'helm-M-x) (global-set-key (kbd "C-x r b") #'helm-filtered-bookmarks) (global-set-key (kbd "C-x C-f") #'helm-find-files)
Then enable helm-mode with:
(helm-mode 1)
Or, enable helm-mode interactively with M-x helm-mode.
helm-mode(helm-mode &optional ARG)
Toggle generic helm completion.
If called interactively, toggle ‘Helm mode’. If the prefix argument is positive, enable the mode, and if it is zero or negative, disable the mode.
If called from Lisp, toggle the mode if ARG is ‘toggle’. Enable the mode if ARG is nil, omitted, or is a positive number. Disable the mode if ARG is a negative number.
The mode’s hook is called both when the mode is enabled and when it is disabled.
All functions in Emacs that use ‘completing-read’, ‘read-file-name’, ‘completion-in-region’ and friends will use helm interface when this mode is turned on.
However you can modify this behavior for functions of your choice with ‘helm-completing-read-handlers-alist’.
Called with a positive arg, turn on unconditionally, with a negative arg turn off. You can toggle it with M-x ‘helm-mode’.
About ‘ido-mode’: DO NOT enable ‘ido-everywhere’ when using ‘helm-mode’. Instead of using ‘ido-mode’, add the commands where you want to use ido to ‘helm-completing-read-handlers-alist’ with ‘ido’ as value.
Note: This mode is incompatible with Emacs23.
| • Customize helm-mode |
helm-completing-read-handlers-alistCompleting read functions for specific Emacs commands.
By default ‘helm-mode’ use ‘helm-completing-read-default-handler’ to provide helm completion in each ‘completing-read’ or ‘read-file-name’ found, but other functions can be specified here for specific commands. This also allows disabling helm completion for some commands when needed.
Each entry is a cons cell like (EMACS_COMMAND . COMPLETING-READ_HANDLER) where key and value are symbols.
Each key is an Emacs command that use originaly ‘completing-read’.
Each value maybe a helm function that takes same arguments as ‘completing-read’ plus NAME and BUFFER, where NAME is the name of the new helm source and BUFFER the name of the buffer we will use, but it can be also a function not using helm, in this case the function should take the same args as ‘completing-read’ and not be prefixed by “helm-”.
‘helm’ will use the name of the command calling ‘completing-read’ as NAME and BUFFER will be computed as well with NAME but prefixed with “*helm-mode-”.
This function prefix name must start by “helm-” when it uses helm, otherwise ‘helm’ assumes the function is not a helm function and expects the same args as ‘completing-read’, this allows you to define a handler not using helm completion.
Example:
(defun foo/test () (interactive) (message “%S” (completing-read “test: ” ’(a b c d e))))
(defun helm-foo/test-completing-read-handler (prompt collection predicate require-match initial-input hist def inherit-input-method name buffer) (helm-comp-read prompt collection :marked-candidates t :name name :buffer buffer))
(add-to-list ’helm-completing-read-handlers-alist ’(foo/test . helm-foo/test-completing-read-handler))
We want here to make the regular ‘completing-read’ in ‘foo/test’ return a list of candidate(s) instead of a single candidate.
Note that this function will be reused for ALL the ‘completing-read’ of this command, so it should handle all cases. E.g., if first ‘completing-read’ completes against symbols and second ‘completing-read’ should handle only buffer, your specialized function should handle both.
If the value of an entry is nil completion will fall back to Emacs vanilla behaviour. Example:
If you want to disable helm completion for ‘describe-function’, use:
(describe-function . nil)
Ido is also supported, you can use ‘ido-completing-read’ and ‘ido-read-file-name’ as value of an entry or just ’ido. Example: Enable ido completion for ‘find-file’:
(find-file . ido)
same as
(find-file . ido-read-file-name)
Note that you don’t need to enable ‘ido-mode’ for this to work, see ‘helm-mode’ documentation.
To customize the completion interface or disable completion for
specific commands in helm-mode, edit
helm-completing-read-handlers-alist. See C-h v
helm-completing-read-handlers-alist for details.
| • Use helm-mode and ido-mode |
Up: Customize helm-mode [Contents][Index]
To use
Ido
for some commands and Helm for others, do not enable
ido-mode. Instead, customize helm-completing-read-handlers-alist
to specify which command uses Ido.
For example, suppose we want find-file-read-only to use Ido and
find-file to use Helm. Then:
helm-mode.
helm-mode customize group, add a key to
helm-completing-read-handlers-alist for find-file-read-only
with value ‘ido’, i.e.
(find-file-read-only . ido)
With helm-mode active, to use Emacs default completion instead of
either Helm or Ido, use nil for the key value:
(find-alternate-file . nil)
Next: Helm Workflow for Files Directories and Buffers, Previous: Helm Mode, Up: Top [Contents][Index]
| • linum-relative |
(helm-linum-relative-mode 1) enables linum-relative in Helm. Helm
buffers then display line numbered candidates before and after the
current candidate (highlighted line). C-x <n> jumps to ‘n’ lines
before, before, and C-c <n> jumps to ‘n’ lines after, the current
candidate.
Next: Quick Try with ‘emacs-helmsh’, Previous: Helm With Other Emacs Extensions, Up: Top [Contents][Index]
Other quick jumping off features of helm-find-files:
helm-browse-project) shows buffers and files in the
project.
When using ‘helm-ls-git’13 and ‘helm-ls-hg’14 , files under version control have a corresponding backend indicator.
helm-find-files
file-name-history)
helm-find-files
Next: How to report Helm Bugs, Previous: Helm Workflow for Files Directories and Buffers, Up: Top [Contents][Index]
To try Helm with a default configurations in a minimal Emacs, run the provided ‘emacs-helm.sh’ script in Helm’s installation directory. If installed through the Emacs package manager,
~/.emacs.d/elpa/helm-<VERSION>/emacs-helm.sh
‘emacs-helm.sh’ should also be used when reporting bugs.
Note: If you have installed from Melpa, for convenience, consider creating a symlink of ‘emacs-helm.sh’ to e.g ‘~/bin’, if you have installed from source (make && sudo make install) a symlink named ‘helm’ have already been created.
Note: For people using a non standard Elpa directory emacs-helm.sh may fail because it doesn’t find its dependency (emacs-async), here’s how you can do:
cd /your/path/to/helm make # If not already done. EMACSLOADPATH="../emacs-async:" ./emacs-helm.sh
But normally ‘emacs-helm.sh’ should work out of the box with installations of emacs-async= done with package.el, straight.el or from source with the Makefile.
Next: Useful links, Previous: Quick Try with ‘emacs-helmsh’, Up: Top [Contents][Index]
| • Confirming bugs | ||
| • Reporting bugs |
Next: Reporting bugs, Up: How to report Helm Bugs [Contents][Index]
To confirm that a bug is, in fact, a Helm problem, it is important to replicate the behavior with a minimal Emacs configuration. This precludes the possibility that the bug is caused by factors outside of Helm.
The easiest and recommended way to do so is through the ‘emacs-helm.sh’ script.
| • ‘emacs-helm.sh’ | ||
| • ‘emacs -Q’ |
Next: ‘emacs -Q’, Up: Confirming bugs [Contents][Index]
If your system supports it, you should run the ‘emacs-helm.sh’ script to start an Emacs instance with minimal, Helm-specific configuration.
This is useful for debugging, and easier than starting Emacs with ‘emacs -Q’ and configuring Helm from scratch.
If Helm is installed via MELPA, the ‘emacs-helm.sh’ script should be located at ‘~/.emacs.d/elpa/helm-<version>/emacs-helm.sh’.
Of course you have to cd to your helm directory and run the script from there, an alternative is symlinking it to somewhere in your ‘PATH’ e.g. “~/bin” (See note at bottom for those that have installed from source with ‘make’).
You can use the -h argument for help:
$ helm -h Usage: helm [-P} Emacs path [-h} help [--] EMACS ARGS
If your emacs binary is not in a standard place i.e. “emacs”, you can specify the path with “-P”.
Note: If you have installed Helm from Git and used ‘make && sudo
make install’ you can run directly ‘helm’ at command line from any
place i.e. no need to cd to helm directory.
Previous: ‘emacs-helmsh’, Up: Confirming bugs [Contents][Index]
If you cannot run the ‘emacs-helm.sh’ script, be sure to reproduce the problem with ‘emacs -Q’, then installing Helm as described in the Install section.
Previous: Confirming bugs, Up: How to report Helm Bugs [Contents][Index]
To report a bug, open an issue. Be sure that you’ve confirmed the bug as described in the previous section, and include relevant information for the maintainer to identify the bug.
| • Version info |
Up: Reporting bugs [Contents][Index]
When reporting bugs, it is important to include the Helm version number, which can be found in the helm-pkg.el file.
Next: Main Index, Previous: How to report Helm Bugs, Up: Top [Contents][Index]
Next: Key Index, Previous: Useful links, Up: Top [Contents][Index]
| Jump to: | E H |
|---|
| Index Entry | Section | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| | |||
| E | |||
| emacs-helm.sh: | Minimal setup using source | ||
| emacs-helm.sh: | Quick Try with ‘emacs-helmsh’ | ||
| | |||
| H | |||
| helm native commands: | Introduction | ||
| helmized commands: | Introduction | ||
| | |||
| Jump to: | E H |
|---|
Next: Command and Function Index, Previous: Main Index, Up: Top [Contents][Index]
Next: Variable Index, Previous: Key Index, Up: Top [Contents][Index]
Previous: Command and Function Index, Up: Top [Contents][Index]
This is not a complete index of variables and faces, only the ones that are mentioned in the manual. For a more complete list, use M-x org-customize and then click yourself through the tree.
| Jump to: | H |
|---|
| Jump to: | H |
|---|
https://github.com/raxod502/straight.el
https://github.com/emacs-helm/helm/releases
Don’t forget the final ‘:’ to use an absolute path (like ‘/home/you/foo/bar:’) instead of an abbreviated path like (‘~/foo/bar:’), specify ‘EMACSLOADPATH’.
Helm uses async package to compile itself from Melpa. Ensure
that async-bytecomp-package-mode is enabled by default. If this
isn’t so, add helm to async-bytecomp-allowed-packages.
Different way of invoking commands